Abstract
Introduction: A common initial treatment approach for PTLD includes reduction of immunosuppression (RIS) and single-agent rituximab, followed by sequential chemoimmunotherapy for non-responding patients (pts). However, in relapsed disease, there is less consensus on optimum therapy. Moreover, there are very limited data regarding the use of chimeric antigen receptor (CAR) T-cell therapy in relapsed/refractory SOT-related PTLD, despite its documented efficacy and tolerability in large B-cell lymphoma (LBCL).
Methods: We conducted a multicenter, retrospective, RWE analysis of adults who had SOT-associated PTLD. We obtained baseline clinical features at diagnosis of PTLD including prior organ transplant, immunosuppression usage, international prognostic index (IPI), EBV status, treatment course, response to therapy, and clinical course with CD19 CAR-T. Post-CAR-T survival analyses were performed using Kaplan-Meier with comparison by response using log rank.
Results: A total of 20 pts across 8 U.S. academic centers were included in the analysis. Pathology was monomorphic B-cell PTLD in all cases; most pts had diffuse LBCL NOS, with 3 high-grade BCL NOS cases. Prior SOT included 15 kidney transplants (75%), 3 liver (15%), 1 intestinal (5%), and 1 heart transplant (5%). Median time from SOT to PTLD diagnosis was 107 months (mos) (5-379). The median age at time of CART was 55 years (31-75 years) with 4 pts (22.2%) aged >70 years (see Table). The tumor EBV status was negative in 16 pts (80%), positive in 1 (5%), and unavailable in 3 pts (15%). The IPI score upon relapse prior to CAR-T therapy was 3-5 among 14 pts (70%) and 0-2 for the other 6 pts (30%). Most of the pts had stage III-IV disease (95%), and elevated LDH (80%) prior to CAR-T. There were also 5 pts (25%) with >1 site of extranodal involvement, and 1 pt (5%) had secondary central nervous system involvement.
For initial therapy of PTLD, 4 pts (20%) received rituximab alone, 12 (60%) had R-CHOP, and 4 (20%) received dose-adjusted R-EPOCH. The median number of prior therapies prior to CAR-T was 2 (1-4); bridging therapy prior to CAR-T are listed in the Table. Immunosuppression was stopped completely prior to CAR-T infusion in 15 (75%) pts, with prednisone alone continued for 3. For CAR-T therapy, 13 pts (65%) received tisagenlecleucel and 7 pts (35%) axicabtagene ciloleucel; 18 received commercial product and 2 were treated on a clinical trial. For tolerability, 16 (80%) pts experienced cytokine release syndrome (CRS): 9 (45%) grade (G) 1, 5 (25%) G2, and 1 (5%) each for G3 and G4. The immune effector cell-associated neurotoxicity syndrome (ICANS) was observed in 14 (70%) pts: 2 (10%) G1, 5 (25%) G2, 5 (25%) G3, and 2 (10%) G4. There were 2 (10%) pts with treatment-related mortality (TRM) at 1.5 and 4.5 mos post-CAR-T (1 pneumonia/sepsis and 1 encephalopathy). The overall response rate was 65%, with 50% complete remission (CR) and 20% stable disease.
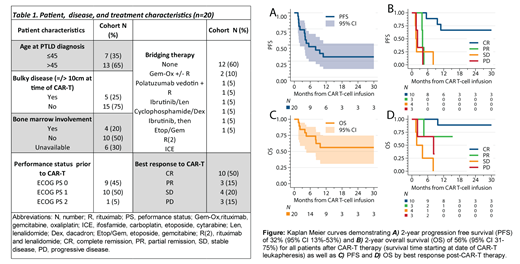
13 of 15 pts resumed immunosuppression post-CAR-T after a median of 2.2 mos (1-14). Of these pts, 8 were started on steroids; 2 on tacrolimus, 1 both steroid and tacrolimus; 1 everolimus; and 1 on sirolimus. 3 pts (15%) experienced allograft rejection after CAR-T, all of which were kidney SOTs occurring at 1, 4, and 14.6 mos after CAR-T infusion; 1 pt died due to disease progression (1.5 mos) and the 2 other pts required hemodialysis. CRS and ICANS scoring for these 3 pts were 0, 0, 2, and 1, 3, 1, respectively, and all were off immunosuppression at time of rejection. Overall, at a median follow-up of 25 mos (5-112), 13 pts (65%) had progression of disease or TRM, and 7 pts (35%) remained in remission (Figure A/B). Additionally, as highlighted in Figure C/D, all non-relapsing pts had achieved CR with CAR-T therapy (7/10 CR remain in remission), which was strongly associated with outcomes (PFS HR 0.03 (95% CI 0.00-0.29), P=0.002; and OS HR 0.06 (95% CI 0.01-0.57), P=0.014).
Conclusions: This RWE provides the largest analysis to date of CD19 CAR-T therapy in relapsed/refractory SOT-related LBCL PTLD. We found that rates of CAR-T-related CRS and neurologic events appeared comparable with previous non-PTLD CAR-T data. Furthermore, 50% of SOT-PTLD pts obtained a CR, with approximately one-third of pts sustaining long-term remission, and achievement of CR was a critical factor associated with survival. Finally, with abrogation of immunosuppression prior to CAR-T, and careful resumption post-therapy, organ preservation was achieved in most pts.
Ghobadi: Wugen: Consultancy; Atara: Consultancy; Amgen: Consultancy, Research Funding; Kite, a Gilead Company: Consultancy, Honoraria, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy. Lazaryan: Kadmon: Consultancy; Avrobio: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees; Humanigen: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees. Jacobson: Precision Biosciences: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel support; Kite, a Gilead Company: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel support; AbbVie: Consultancy, Honoraria; Pfizer: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel support, Research Funding; Celgene: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel support; Nkarta: Consultancy, Honoraria; Novartis Pharmaceuticals Corporation: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel support; Lonza: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel support; Humanigen: Consultancy, Honoraria, Other: Travel support; Axis: Speakers Bureau; Clinical Care Options: Speakers Bureau. Naik: Sanofi: Other: Virtual Advisory Board Member ; Takeda: Other: Virtual Advisory Board Member ; Kite: Other: Virtual Advisory Board Member. Olszewski: TG Therapeutics: Research Funding; PrecisionBio: Research Funding; Celldex Therapeutics: Research Funding; Acrotech Pharma: Research Funding; Genentech, Inc.: Research Funding; Genmab: Research Funding. Nastoupil: TG Therapeutics: Honoraria, Research Funding; Genentech: Honoraria, Research Funding; Janssen: Honoraria, Research Funding; Gilead/Kite: Honoraria, Research Funding; ADC Therapeutics: Honoraria; Denovo Pharma: Other: DSMC; Epizyme: Honoraria, Research Funding; Bristol Myers Squibb/Celgene: Honoraria, Research Funding; Takeda: Honoraria, Other: DSMC, Research Funding; IGM Biosciences: Research Funding; Caribou Biosciences: Research Funding; Bayer: Honoraria; MorphoSys: Honoraria; Pfizer: Honoraria, Research Funding; Novartis: Honoraria, Research Funding. Ahmed: Tessa Therapeutics: Membership on an entity's Board of Directors or advisory committees, Research Funding; Seagen: Research Funding; Merck: Research Funding; Xencor: Research Funding.

This feature is available to Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account Close Modal